What is physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy helps restore movement and function to as near normal as possible when someone is affected by injury, illness or by developmental or other disability.
And as a healthcare profession, physiotherapy’s science foundation covers a broad and varied range of work which involves working with people to promote their own health and well being.
They combine their knowledge, skills and approach to improve a broad range of physical problems associated with different ‘systems’ of the body. In particular they treat:
- neuromuscular (brain and nervous system)
- musculoskeletal (soft tissues, joints and bones)
- cardiovascular and
- respiratory systems (heart and lungs and associated physiology). Link to www.csp.org.uk
Treatments can include:
- pain relief
- regaining range of motion and enhancing muscle strengh
- soft tissue work
- Neuro rehabilitaion
- Electrotherapy
- Manipulation
- Restoring mobility and facilitating independence
Chronic Pain – What Causes Chronic Pain?
Chronic pain can be caused by many different factors. Often conditions that accompany normal aging may affect bones and joints in ways that cause chronic pain. Other common causes are nerve damage and injuries that fail to heal properly. Some kinds of chronic pain have numerous causes. Back pain, for example, may be caused by a single factor, or any combination of these factors: Years of poor posture Improper lifting and carrying of heavy objects Being overweight, which puts excess strain on the joints can also be a factor.
A physiotherapist can help address these issues and give you the tools to manage your condition.
How Is Physiotherapy Used to Treat Pain?
A therapist may focus on decreasing pain with either passive or active therapy.
Examples of passive physical therapy include:
- Heat/ice packs
- TENS units
- Ultrasound
Examples of active physical therapy include:
- Stretching
- Strengthening exercises
- Pain relief exercises
- Low-impact aerobic conditioning
Pain Management and Physiotherapy
Pain relief is often accomplished through physiotherapy, which involves the treatment, healing, and prevention of injuries or disabilities. Physiotherapy helps to relieve pain, promote healing, and restore function and movement.
What is Neurorehabilitation?
Neurorehabilitation is a collection processes that are case specific which focus on aiding a person’s recovery, or help that individual to live a more normal, active, and independent life. The quality of life of a person can be greatly affected by a brain or spinal cord injury, or a medical condition which affects the mobility, cognitive functions, or other physical or psychological processes that have been affected by changes in the nervous system. The goal of neurorehabilitation is to combat those changes and improve quality of life by various therapies.
Conditions Commonly Treated by Neurorehabilitation
- Stroke recovery
- Neuropathies
- Cerebral palsy
- Parkinson’s disease
- Brain injury
- Multiple sclerosis
- Post-polio syndrome
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
How Neurorehabilitation Works
By focusing on all aspects of a person’s wellbeing, neurorehabilitation offers a series of therapies from the psychological to occupational, teaching or re-training patients on mobility skills, communication processes, and other aspects of that person’s daily routine. Neurorehabilitation also provides focuses on nutrition, psychological, and creative parts of a person’s recovery.
What is neurological physiotherapy?
 Neurological physiotherapy is the treatment of patients who have a neurological disorder such as stroke, MS, brain injury or Parkinson’s disease.
Neurological physiotherapy is the treatment of patients who have a neurological disorder such as stroke, MS, brain injury or Parkinson’s disease.
Physiotherapists may specialise in a particular aspect of physiotherapy as their career progresses. A neurological physiotherapist will have gained experience by treating neurological patients and also attending courses specific to neurological physiotherapy to further their knowledge in this area.
How does neurophysiotherapy differ from physiotherapy?
Neurological physiotherapy will specifically assess the problems that result from a neurological disorder. These may include spasticity, weakness, walking problems, balance problems and altered movement patterns.
What does neurological physiotherapy involve?
A neurological physiotherapist will assess a patient fully to determine the main issues causing concern for the patient. Goals will be formulated based on these issues and a treatment plan devised and carried through to address these, aiming to achieve previous functions.
This may take the form of specific analysis of posture and movement, facilitation of return of movement, control of spasticity, exercises to stimulate balance and walking practice.
This is by no means an exhaustive list of treatment principles, but may be some of the main areas a neurological physiotherapist has expertise in.
Manage your neck and back pain
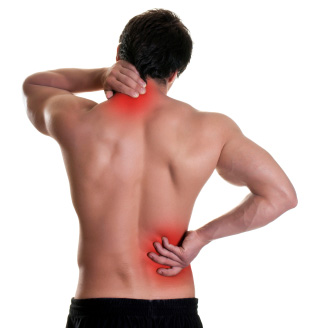 Exercises for the neck and lumbar spine are very important. If done correctly they can increase your range of motion, mobility and strengthen the spine. As you increase the mobility in your spine, you will notice greater range of motion and movement with less stiffness. With less stiffness there is usually less pain. A physiotherapist can guide you in the selection of the correct exercises to manage your condion.
Exercises for the neck and lumbar spine are very important. If done correctly they can increase your range of motion, mobility and strengthen the spine. As you increase the mobility in your spine, you will notice greater range of motion and movement with less stiffness. With less stiffness there is usually less pain. A physiotherapist can guide you in the selection of the correct exercises to manage your condion.
Points to Consider
An important aspect to keep in mind about physiotherapy is that each individual is different and may respond differently to therapy. People have different types of bodies, different patterns of movement, different alignments, and different habits. Physiotherapists can monitor each individual and attempt to correct improper habits, alignments, and movement patterns.
Don’t suffer in silence – live again.
Don’t suffer in silence – live again.
You can view and leave testimonials of my work at blogrectory





